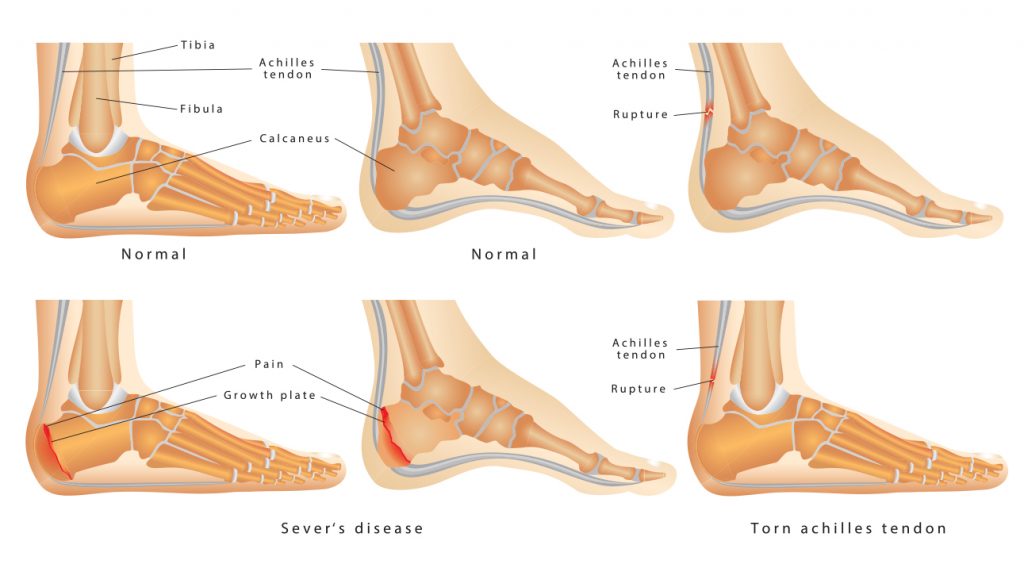
The Achilles tendon is the thick cord-like structure that attaches the calf muscle to the heel bone. It is the largest tendon in the body and is able to withstand a large amount of tensile force making it an important structure for walking, jumping and running.
ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY
What is the Achilles tendon?
What is the Achilles tendinopathy?
Achilles tendinopathy (in the past it has been referred to as tendinosis or tendinitis) is a common overuse injury affecting the Achilles tendon. This occurs when the Achilles tendon is placed under repetitive stress with inadequate healing time. Small tears (micro-trauma) form which become painful. It’s more common in those who change their walking habits, run frequently or participate in running/jumping sports.
Achilles tendinopathy can also be a predisposing factor an Achilles tendon rupture which occurs very suddenly and is usually described as large ‘pop’.
Risk factors for Achilles tendinopathy
- Poor calf muscle strength and flexibility
- Increase in training load/physical activity levels
- Over-weight
- Type 2 diabetes
What are the causes of Achilles tendinopathy?
There are a number of causes of Achilles tendinopathy some include:
- Overuse injury – More commonly seen when there has been a sudden increase in physical activity or sports and inadequate rest/recovery
- Footwear – a change in footwear while walking/running can increase the chance of developing the injury
- Training program – A poor training regime e.g. inadequate recovery times between training sessions or a sudden increase in intensity or frequency of your training. Additionally, poor running technique can also contribute to injury
- Foot biomechanics – the posture of your foot can place more strain on the Achilles tendon e.g. flat feet or pronated feet (feet turned inwards)
What are the symptoms of Achilles tendinopathy?
The symptoms of Achilles tendinopathy usually come on slowly and build up gradually. Common symptoms include:
- Pain and stiffness around the Achilles tendon or back of the heel
- Morning stiffness
- Pain after activity
- The Achilles may be pain free when you first start to exercises
How is an Achilles tendinopathy treated?
If you suspect you have Achilles tendinopathy, see your physiotherapist for further assessment. They will ask questions regarding your symptoms and perform a physical examination to ensure you receive the adequate rehabilitation.
Treatment may include:
- Advice on how to best modify your activity levels, generally complete rest is not advised
- Hands-on treatment to reduce associated muscle tension
- Tailored strengthening/stretching exercises
- Walking/running assessment to evaluate whether orthotics or different footwear may be appropriate
For those getting back to running, once you are on the right track, speak to your physiotherapist about having a running assessment to maximise your progression and optimise your performance.

